AnyWave:WriteMatlabScripted
Contents
Introduction
This section targets people who have a good knowledge and practice of the MATLAB programming language.
The purpose is to explain how to write a MATLAB function that will be the heart of a plug-in executed in MATLAB by AnyWave.
We will also explain how to create a text file to describe our plug-in to AnyWave
The AnyWave-MATLAB API (Application Programming Interface) which is a set of MATLAB functions, will be described in details, with examples to illustrate their use.
Requirements
MATLAB software must be installed on the computer. AnyWave should be able to detect the installation by itself. However, in some special cases, MATLAB could be installed on a custom path AnyWave may not check. In that case, the user must specify the path to MATLAB in AnyWave by changing options in the Preferences settings.
NB: on Linux, csh must be installed at /bin/csh, or the MATLAB Engine API used by AnyWave will not function, and AnyWave will report "Failed to connect to MATLAB!" in the corresponding Process log.
Where to start?
The first thing to do is to create the basic structure for a plug-in.
A MATLAB Scripted plug-in is very simple: it is a folder containing at least two files.
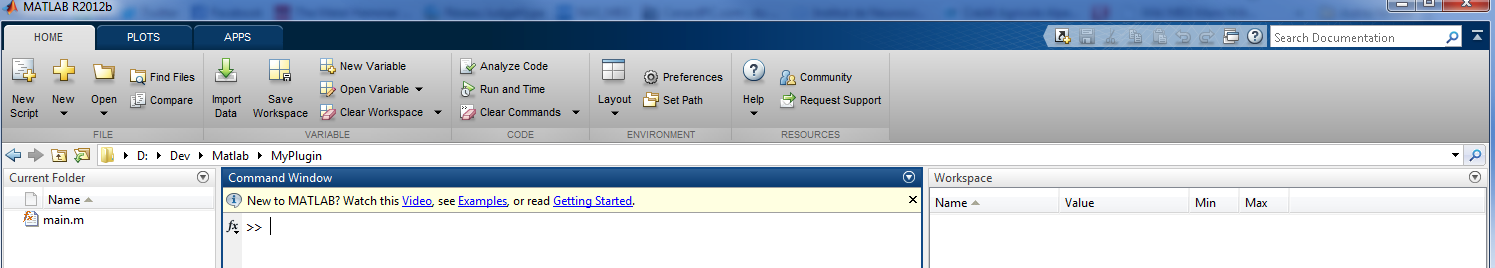
Let's begin by creating a folder (called MyPlugin) somewhere on the computer.
This can be done in MATLAB: create a folder and create a new function called main in that folder.
The main function is MANDATORY. It will be the main function AnyWave will call to execute our plugin.
As shown in the image above, a MyPlugin folder has been created and a main function was added.
We are now ready to write our first Matlab plug-in!!
Refer to the AnyWave-MATLAB functions section to learn how to program a plug-in that will communicate with AnyWave.
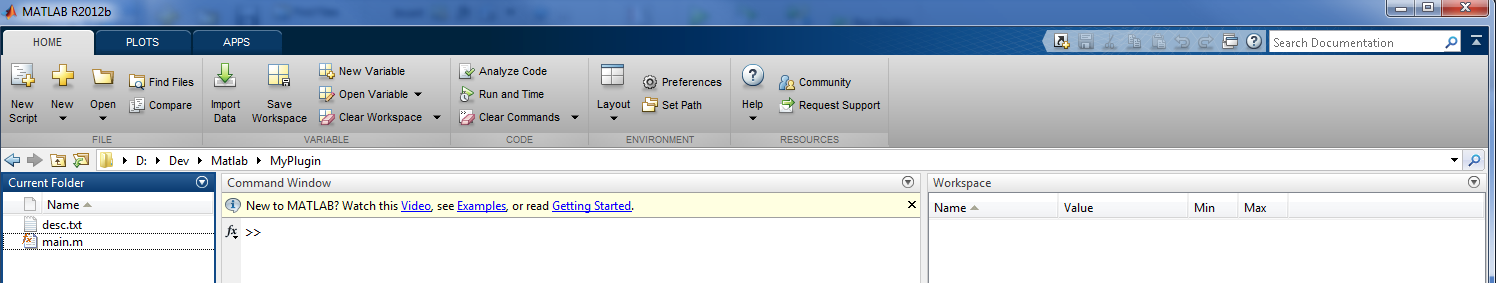
Writing the desc.txt file
We have written the MATLAB code and now all we have to do is to create a descriptive text file to inform AnyWave about our plug-in.
Let's dot it in Maltab:
The file must be named desc.txt and may looks like:
name = My Matlab Plugin description = I am a plug-in written in Matlab category = Process:MATLAB:My MATLAB Plugin
The category line is optional. It tells AnyWave where the plug-in will appear in the menus. Here we decided to caterogize it as a Process, with a sub category called MATLAB. Finally, the plug-in name will be My MATLAB Plugin.
The category feature is usefull to separate plug-in that won't really do some calculation but convert data to another format or launch external tools. It could also be useful to classify signal processing algorithms.
Three category keywords are recognized:
- Process : The plug-in will be set in the Processes menu with a subcategory and a name, for example 'Process:Correlation:Compute correlation'
- File: The plug-in will be set in the File Menu under the Export sub-menu. Example : 'File:Export to MATLAB'
- View: The plug-in will be set in the View Menu. Example : 'View:Launch 3D viewer'
If no category is specified, AnyWave will set the plug-in in the Processes menu using the name defined in the file.
Copy the plug-in to the right location
We are ready to add the plug-in to AnyWave.
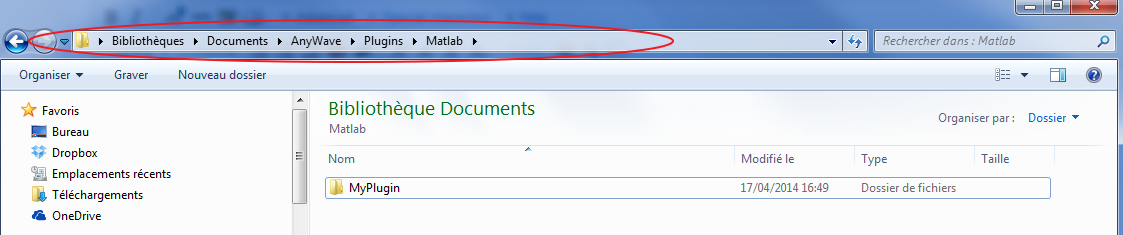
Copy the folder MyPlugin to your user's AnyWave plugins directory. Remember to place it in the Matlab subfolder. For example on Windows:
As you can see MyPlugin is located in the user's AnyWave path for Matlab Scripted plug-ins.
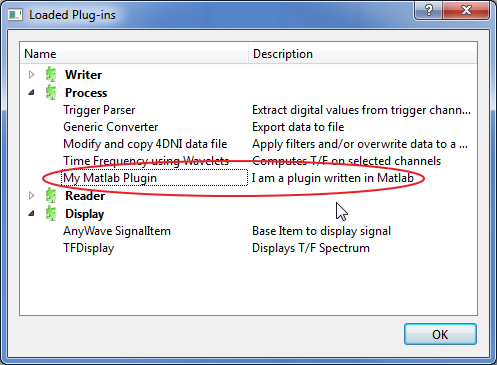
Use the plug-in in AnyWave
Launch AnyWave: the plug-in should be shown as available.
AnyWave-MATLAB functions
The table below shows a summary of all MATLAB functions available when writing a MATLAB Scripted plug-in:
Note: All AnyWave MATLAB functions start with 'aw_' to avoid confusions with other MATLAB functions.
| Function | Short description |
|---|---|
| aw_getplugininfo | Returns useful information about the plugin. |
| aw_getdata | Returns data from AnyWave. |
| aw_getmarkers | Returns markers from AnyWave. |
| aw_addmarkers | Sends markers to AnyWave. |
aw_getplugininfo
function [ infos ] = aw_getplugininfo() %aw_getplugininfo returns information about the input set for the plugin. % infos = aw_getplugininfo(); % % returns a structure with the following fields: % .labels % labels of channels set as input for the plugin. % .refs % references of channels: Empty strings for monopolar channels. % .max_sr % maximum sampling rate in Hz. % .total_duration % the total duration in seconds of the data. % .temp_dir % the path to a temporary directory created by AnyWave for the % plugin. % end
aw_getdata
function [ channels ] = aw_getdata(cfg ) %aw_getdata request data from AnyWave % channels = aw_getdata(cfg) % returns channels' data according to the settings defined in cfg structure. % % cfg may contain the following fields: % % cfg.start = 10.; % starting position in seconds of requested data. % if this field is not specified, AnyWave will return data starting % at position 0s. % cfg.duration = 20.; % duration of requested data in seconds. % if this field is not specified, AnyWave will return ALL the % available data. % cfg.labels = {'A1', 'A2'}; % cell array of strings to identify the required channel labels. % if no labels are specified, AnyWave will return the current selected % channels set as input for the plugin. % % cfg.filtering = 'no'; % specifies that we don't want AnyWave to filter the data. % cfg.filtering = 'yes'; % specifies that we want data to be filtered. % Note: % if the filtering field is not specified, the data will be filtered by % AnyWave using the current user defined settings. % % cfg.eeg_lp = 10.; requires filtering = 'yes'. % specifies that we want EEG data with low pass filter of 10Hz. % cfg.eeg_hp = 1.; requires filtering = 'yes'. % specifies that we want EEG data with high pass filter of 1Hz. % cfg.meg_lp = 10.; requires filtering = 'yes'. % specifies that we want MEG data with low pass filter of 10Hz. % cfg.meg_hp = 1.; requires filtering = 'yes'. % specifies that we want MEG data with high pass filter of 1Hz. % % cfg.decimate = 8; % specifies that we only take 1 sample of data every 8 samples. % %Output: % channels is an array of strucrures with the following fields: % .label; % a string representing the channel's label. % .ref; % a string representing the reference channel. Can be empty. % .data; % a data vector containing the samples. % .sr; % the sampling rate of data. % .hpf; % the High Pass filter set. % .lpf; % the Low Pass filter set. end
Example:
function main % request 10 seconds of data starting at 2.5s cfg = []; cfg.start = 2.5; cfg.duration = 10; channels = aw_getdata(cfg); % request raw data (with no filtering) cfg = []; cfg.start = 2.5; cfg.duration = 10; cfg.filtering = 'no'; channels = aw_getdata(cfg); % request data with low pass filter of 25Hz on EEG channels cfg = []; cfg.start = 2.5; cfg.duration = 10; cfg.filtering = 'yes'; cfg.eeg_lp = 25; channels = aw_getdata(cfg); end
aw_addmarkers
function aw_addmarkers(markers) %aw_addmarkers add new markers to AnyWave % aw_addmarkers(markers) % % markers is an array of structs. Each element is a marker to be added. % % See also AwMarker % % end function [ marker ] = AwMarker( label, position, duration, value, targets) % defines the structure for a marker % % marker.label % the label for the marker. % marker.position % the position in seconds from the beginning of data. % marker.duration % the duration in seconds. Can be 0 if the marker is just a position % in time. % marker.value % the value associated to the marker. -1 indicates that no value is % set. % marker.targets % a cell array containing the targeted channels. Empty if the marker % is global. marker.label = label; marker.position = position; marker.duration = duration; marker.value = value; marker.targets = targets; end
Example:
function main % % add one marker labeled spike at position 3s. % marker.label = 'spike'; marker.position = 3; % send the marker to AnyWave aw_addmarkers(marker); % add two markers with value and targeted channels markers(1).label = 'spike'; markers(1).position = 3; markers(1).value = 2; markers(1).targets = {'A2'}; % this marker is targeting the channel named A2 markers(2).label = 'selection'; markers(2).position = 15; markers(2).duration = 1.5; % this marker is a selection of 1.5s starting at position 15s. % no targets are specified, the marker is GLOBAL % send the markers to AnyWave aw_addmarkers(markers); end
AwGetMarkers(<keyword>, <keyword parameter>)
This function will return Markers currently present in AnyWave. If no parameters are specified, the function returns all the markers handle by AnyWave.
The Markers are returned as an array of structures. Let see the format of a marker structure:
marker.label = 'Marker Label'; marker.start = 0.; % position in seconds from the beginning of the file. marker.duration = 0.; % duration in seconds. If 0. then the marker is a single marker which marks an event in time. marker.value = -1; % Associated value. % The value is an integer (INT16). -1 indicates that no value is currently associated with the marker. marker.channels = {'A1', 'A2'}; % a Cell array of strings indicating the channels that are targeted by the marker. % Can be empty if the marker is global to all channels.
Optional parameters
It is possible to only ask for a subset of the markers currently active in AnyWave. The keyword parameter permits to ask for markers references by their values or by theirs labels.
keyword = 'By Value'
This indicates that we want markers which have a specified value. The second parameter must be the value.
Example:
markers = AwGetMarkers('By Value', 10); % markers will contain structures corresponding to markers with a value 10 % ATTENTION : markers can be an empty array if no markers matches the request.
keyword = 'By Label'
This indicates that we want markers which have a specified label. The second parameter must be the label.
Example:
markers = AwGetMarkers('By Label', 'Stimulus 1'); % markers will contain structures corresponding to markers with a label set to Stimulus 1 % ATTENTION : markers can be an empty array if no markers matches the request.
AwSendMessage(message)
This function sends a text message to AnyWave. The message will appear in the Processes console in AnyWave and also in the plugin's log.
Example:
channels = AwGetData(0, -1); % get all data for (i=1:numel(channels) AwSendMessage(sprintf('Processing channel %d', i)); % do something end
AwIsProcessTerminated
This function will return true or false depending on the action of the user about the currently running plug-in.
This function is usefull when processing heavy and long calculations. If the user want to cancel the current processing, it may be suitable to cancel the current calculation running in MATLAB as well.
Example:
channels = AwGetData(0, -1); % get all data % for (i=1:numel(channels) if (~AwProcessIsTerminated()) % do some heavy calculation on a data contained in channel end end