Difference between revisions of "AnyWave:WriteMatlabScripted"
(→AnyWave-MATLAB functions) |
(→AwAddMarker(lable, value, position, duration, )) |
||
| Line 224: | Line 224: | ||
==AwGetFilePath()== | ==AwGetFilePath()== | ||
This function returns the complete path to the current data file open by AnyWave. That could be usefull, for example, if we want to copy and rename the data file. | This function returns the complete path to the current data file open by AnyWave. That could be usefull, for example, if we want to copy and rename the data file. | ||
| − | ==AwAddMarker( | + | ==AwAddMarker(label, value, position, duration, <targeted channels>)== |
| − | + | AnyWave is able to receive markers as output of a plug-in. This function will add a marker to the list of output parameters that will be handle by AnyWave when the plug-in has terminated.<br/> | |
===Parameters=== | ===Parameters=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 10:20, 18 April 2014
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Where to start?
- 3 Writing the desc.txt file
- 4 Copy the plug-in to the right location
- 5 Use the plug-in in AnyWave
- 6 AnyWave-MATLAB functions
Introduction
This section targets people who have a good knowledge and practice of the Matlab programming language.
The purpose is to explain how to write a Matlab function that will be the heart of the plug-in.
We will also explain how to create a text file to describe our plug-in to AnyWave
The AnyWave-Matlab API (Application Programming Interface) which is a set a Matlab functions, will be described in details, with examples to illustrate their use.
Where to start?
The first thing to do is to create the basic structure for a plug-in.
A Matlab Scripted plug-in is very simple, it is a folder containing at least two files.
Let's begin by creating a folder somewhere on the computer, called MyPlugin.
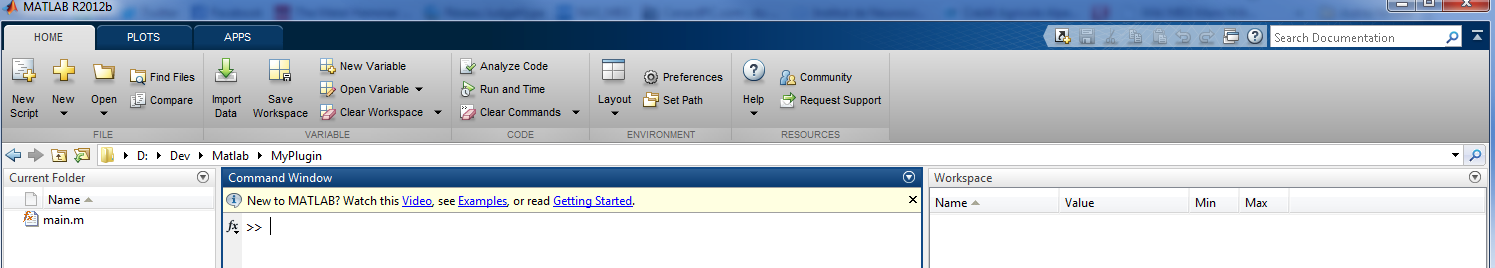
This can be done in MATLAB: create a folder and create a new function called main in that folder.
The main function is MANDATORY. It will be the main function AnyWave will call to execute our plugin.
As shown in the image above, a MyPlugin folder has been created and a main function was added.
We are now ready to write our first Matlab plug-in!!
Refer to the AnyWave-MATLAB functions section to learn how to program a plug-in that will communicate with AnyWave.
Writing the desc.txt file
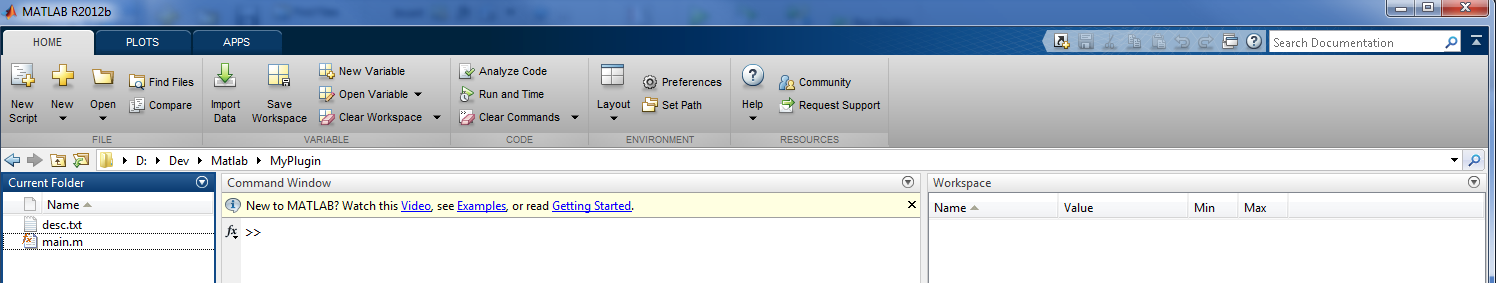
We have written the Matlab code and now all we have to do is to create a descriptive text file to inform AnyWave about our plug-in.
Let's dot it in Maltab:
The file must be named desc.txt and may looks like:
name = My Matlab Plugin description = I am a plug-in written in Matlab
That's enough to make our plugin visible and usable by AnyWave.
Copy the plug-in to the right location
We are ready to add the plug-in to AnyWave.
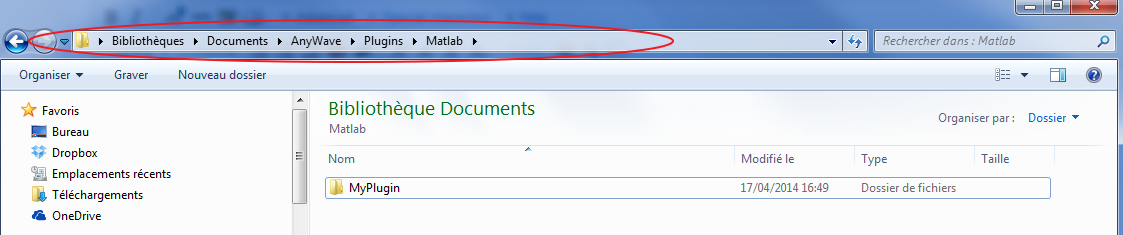
Copy the folder MyPlugin to your user's AnyWave plugins directory. Remember to place it in the Matlab subfolder. For example on Windows:
As you can see MyPlugin in located in the user's AnyWave path for Matlab Scripted plug-ins.
Use the plug-in in AnyWave
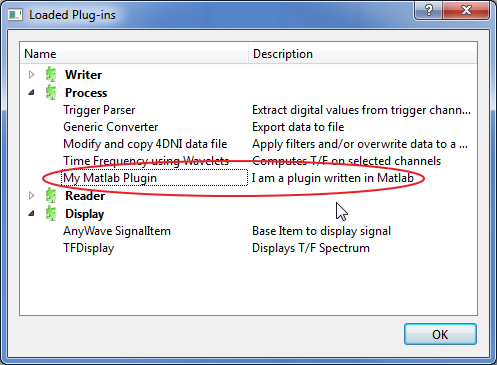
Launch AnyWave, the plug-in should be shown as available.
AnyWave-MATLAB functions
The table below shows a summary of all Matlab functions available when writing a Matlab Scripted plug-in:
Function parameters placed between <> are optional.
Note: All AnyWave Matlab functions begin with Aw. That will avoid confusion and clearly indicates the purpose of these functions.
| Function | Short description |
|---|---|
| AwGetInputChannels() | Get current input channels set by AnyWave for the plug-in. |
| AwGetData(start, duration, <filtering>, <filteringOptions>) | Get the data of the current input channels. |
| AwGetWorkingDir() | Get the full path to a temporary directory created by AnyWave for the plug-in. |
| AwGetFilePath() | Get the full path of the current open data file in AnyWave. |
| AwAddMarker(label, value, position, duration, <targeted channels>) | Add a marker in AnyWave. |
| AwSendMessage(message) | Send a message to AnyWave. The message will be added to the plug-in's log. |
| AwIsProcessTerminated() | Returns true if the process has been aborted by the user in AnyWave. |
AwGetInputChannels()
AnyWave uses channels to represent signals on screen but also as its internal data set.
When a plug-in is launched by AnyWave, a set of input and/or output parameters is defined accordingly to the specific settings for the plug-in.
The default behavior is to set as input channels the current selected channels in AnyWave. If there is no selection, then AnyWave will set all the channels in the current montage as input channels.
AwGetInputChannels() will request the list of input channels for the plug-in. No parameters are required.
AnyWave will send back a structure array containing Matlab structures which match the structure defined by the AwChannel() function.
AwChannel() is provided by AnyWave to easily create a Matlab structure which will be compatible with AnyWave's channels objects.
This function is usefull if you want to get input the channels' informations without requesting for data.
Let's try it in our main function for our plug-in:
function main() %MAIN Summary of this function goes here % Detailed explanation goes here channels = AwGetInputChannels(); disp('Input channels:'); for i=1:numel(channels) fprintf('name: %s', channels(i).name); fprintf('ref: %s', channels(i).ref); fprintf('sampling rate: %g Hz', channels(i).samplingRate); end end
As explained above, the channels variable is a Matlab array of structs filled by AnyWave.
The function will then enumerate the contents of the array.
The structure contains 4 fields but only three are usefull in our case:
1. name is a string and contains the name associated with the channel by AnyWave.
Note that if a reference has been set in AnyWave the name will contain the name of the reference channel (for example: A1 - A2 in a bipolar montage).
2. ref is a string and contains the reference channel set for the current channel. The string is empty if no reference is set.
3. samplingRate is a double value containing the data sampling rate in Hertz.
Note that the messages that usually go to the Matlab Command Window, like those coming from disp() or fprintf() will be available in AnyWave.
AnyWave will get the content of all text outputs from the Matlab script and put it in the process's log.
AwGetData(start, duration, <filtering keyword>, <filtering options>)
As explained in AwGetInputChannels(), AnyWave will set some channels as input for the plug-in. AwGetData() will request data for these channels.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. start | The position in file in seconds. |
| 2. duration | Duration in seconds of the data or -1 to get ALL data in the file. (could be memory consuming). |
| 3. filtering keyword : optional | A string representing filtering options to apply on data. |
| filtering keyword:'No Filtering' | Request data with no filtering: AnyWave will send data as they are in the file. |
| filtering keyword:'User Filtering Options' | Apply specific filtering options on data. That implies the use of the fourth parameter. |
| 4. filtering options : optional | optional if no filtering keyword is set or if the fileting keyword is 'No Filtering'. |
filtering options must be a structure that matches the one generated by the AwFilteringOptions() Matlab function:
function [ foptions ] = AwFilteringOptions() foptions.meg_high = 0.; foptions.meg_low = 0.; foptions.eeg_high = 0.; foptions.eeg_low = 0.; foptions.emg_high = 0.; foptions.emg_low = 0.; end
As you can see above, the AwFilteringOptions function will create a structure with all fields set to zero, which means no filtering on data of all types of channels.
The structure can then be modified to specify custom filtering options.
Note: If no filtering options are specified using the filtering keyword parameter, then the data coming from AnyWave will be filtered as it is defined in AnyWave.
In other words, if you have set filtering options in AnyWave, that filtering options will be applied when requesting for data in the Matlab plug-in.
Examples
Requesting data with AnyWave's current filtering options
function main() %MAIN Summary of this function goes here % Detailed explanation goes here % ask for data, at position 0 and for a duration of 20 seconds. channels = AwGetData(0, 20); % plot only the first channel. plot(channels(1).data); % Wait for the user to close the figure. uiwait(); end
Like in the AwGetInputChannels() example above, channels will be an array of structures containing informations about input channels.
The difference here is that the data are provided by AnyWave. The data vector for a channel is available in the field named data.
In the script above we will get 20 seconds of data from the begining of file, using the current filtering options of AnyWave.
We then plot the data contained in the first channel and wait for the user to close the figure.
Note: uiwait() is mandatory here if you want to see something on the screen when the plug-in will be executed by AnyWave.
This is due to the fact that the Matlab code will not run in the normal Matlab context, with a Command Window and a workspace.
Requesting data using filtering options
function main() % create the filteriong options struct foptions = AwFilteringOptions(); % set specific filtering options % eeg channels only will be filtered. foptions.eeg_high = 45; % High pass filter 45Hz foptions.eeg_low = 5; % Low pass filter 5Hz % get data channels = AwGetData(0, 20, 'User Filtering Options', foptions); % plot only the first channel. plot(channels(1).data); % Wait for the user to close the figure. uiwait(); end
The example above shows how to ask AnyWave to filter data. Note that only the EEG channels will be filtered. That implies that some EEG channels are set as input for the plug-in.
Requesting data with no filtering
function main() channels = AwGetData(0, 20, 'No Filtering'); % plot only the first channel. plot(channels(1).data); % Wait for the user to close the figure. uiwait(); end
Remember: No Filtering means that AnyWave will send data as they are stored in the file.
AwGetWorkingDir()
The function returns a string which is the full path to a temporary folder created by AnyWave for the plug-in.
This is particularly usefull to store temporary files or settings.
Example:
function main() % get input channels channels = AwGetInputChannels(); % save channels to a temporary file save(strcat(AwGetWorkingDir(), '/channels'), 'channels'); end
AwGetFilePath()
This function returns the complete path to the current data file open by AnyWave. That could be usefull, for example, if we want to copy and rename the data file.
AwAddMarker(label, value, position, duration, <targeted channels>)
AnyWave is able to receive markers as output of a plug-in. This function will add a marker to the list of output parameters that will be handle by AnyWave when the plug-in has terminated.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. label | A string to set the marker's label. |
| 2. position | Real scalar value to set the psition in seconds of the marker in the file. |
| 3. value | Integer value (INT16 if possible) associated to the marker. |
| 4. duration | Real scalar value to set the duration of the marker. Could be zero. |
| 5. target channels : optional | A cell array of strings. This parameter is optional. |