Difference between revisions of "AnyWave:H2"
(→A script example) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
h2.step = 2; | h2.step = 2; | ||
h2.maxLag = 0.1; | h2.maxLag = 0.1; | ||
| − | + | ||
h2.matlabFile = "H2output_HP15Hz_LP45Hz"; // defines the Matlab base file name. | h2.matlabFile = "H2output_HP15Hz_LP45Hz"; // defines the Matlab base file name. | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
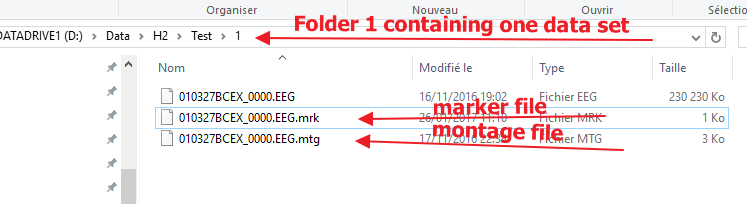
One data sub-folder:<br /> | One data sub-folder:<br /> | ||
[[File:Script_data_folder.png]] | [[File:Script_data_folder.png]] | ||
| + | |||
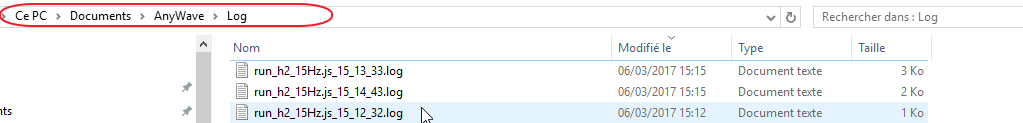
=Check the log file= | =Check the log file= | ||
Every time a process is launched a log file is created by AnyWave.<br /> | Every time a process is launched a log file is created by AnyWave.<br /> | ||
Revision as of 15:27, 16 May 2018
Contents
How to use the plug-in
How to script the H² computation
AnyWave allows to script some compatible plug-ins (and H² is compatible) in order to batch the computations of several data sets.
The script file is a JavaScript file that will be executed by AnyWave this way:
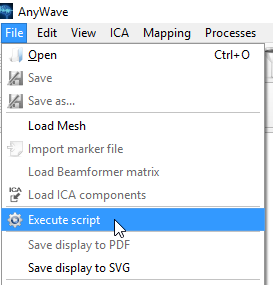
A script example
In our example, we have to compute the H² on three data sets. We first have to select the channels, and one or more time selections for these channels.
To do so, we previously prepared a montage file (that will inform about what channels to use in the computation) and for each data set we also prepared a marker file containing the time selections.
For each data sets, we saved a montage and a marker file along with the data file.
// all AnyWave methods or properties are accessible from the anywave object. var h2 = anywave.getProcess("H2"); // Here we ask anywave for the H2 plugin object. if (h2) { // If the plugin is availablen do the computation // set process parameters. All the parameters are specific to the H2 plugin. h2.windowSize = 4; h2.step = 2; h2.maxLag = 0.1; h2.matlabFile = "H2output_HP15Hz_LP45Hz"; // defines the Matlab base file name. // set files as input (montage and marker files to use) var fi = anywave.getFileInput(); // get the anywave file input object // only take .eeg files as input fi.addFileExtension("*.eeg"); // here we set all the .eeg to be used as data sets. // Define a base folder where to look for data. All sub folders will be explored. fi.setRootDir("d:\\data\\H2"); // Defining how to filter data before processing them. Here we filter SEEG channels only. fi.setFilters("seeg", 45, 15); // run the H2 process on data anywave.runProcess(h2, fi); // Change filter options and rerun the H² process fi.setFilters("seeg", 0, 15); h2.matlabFile = "H2output_HP15Hz"; // change the output matlab file to reflect the filter options anywave.runProcess(h2, fi); // run the plugin again. }
You may have noticed that the script did not mention a montage or a marker file. That is due to the root dir properties we defined.
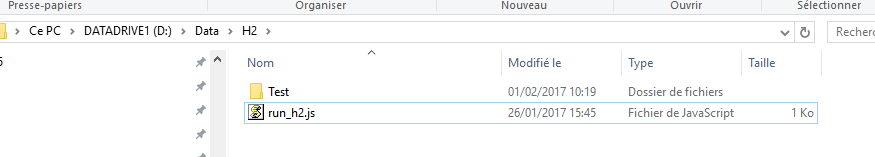
Using a root dir will trigger a recursive folder exploration to find the data set files (using the extension specified.).
When a data file is found matching the extensions, then AnyWave will also look for a marker file and a montage file in the same directory.
So, a good practice is to prepare your data sets using different folders under a root directory and to put a marker and a montage file along with all your data files.
A root folder:
One data sub-folder:
Check the log file
Every time a process is launched a log file is created by AnyWave.
This is also the case for scripted execution.
Check for log files on the Log subfolder of AnyWave: