Difference between revisions of "Welcome"
(sponsors) |
|||
| (54 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | __NOTOC__ | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
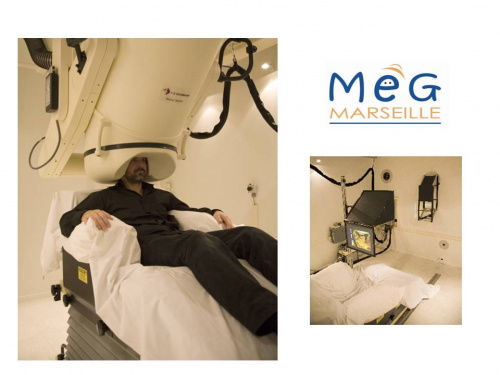
= The Marseille MEG platform.= | = The Marseille MEG platform.= | ||
[[File:MEG figure1.jpg||500px|left]] | [[File:MEG figure1.jpg||500px|left]] | ||
| − | + | Magnetoencephalography (MEG) consists in recording brain magnetic activity. This activity is the counterparts of the electrical activity that originate from the brain, the well-known EEG. These techniques are the only ones that are directly related to the neural activity and have enough time resolution to track brain activity. One of the great advantages of the MEG other EEG is the very small effect of the conductivity of the different media of the head, especially the skull, compared to EEG. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | Magnetoencephalography (MEG) consists in recording brain magnetic activity. This activity is the counterparts of the electrical activity that originate from the brain, the well-known EEG. These techniques are the only ones that are directly related to the neural activity and have enough time resolution to track brain activity. One of the great advantages of the MEG other EEG is the very small effect of the | + | |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | The MEG laboratory of Marseille uses a 248 magnetometers MEG system (4D Neuroimaging magnes 3600), installed within the Neurophysiology department of Timone hospital (Head: F. Bartolomei). The system was co-financed by: Conseil Régional PACA, Conseil Général 13, Conseil Général 06, Marseille Provence Métropole, INSERM, CNRS, INRIA. It is currently co-financed by Aix-Marseille Université (though France Life Imaging) and INSERM. | + | The MEG laboratory of Marseille uses a 248 magnetometers MEG system (4D Neuroimaging magnes 3600). It is part of the [https://ins-amu.fr/ Institut de Neurosciences des Systèmes] (INS, Head V. Jirsa), and is installed within the Neurophysiology department of the Timone hospital (Head: F. Bartolomei). The system was co-financed by: Conseil Régional PACA, Conseil Général 13, Conseil Général 06, Marseille Provence Métropole, INSERM, CNRS, INRIA. It is currently co-financed by Aix-Marseille Université (though France Life Imaging) and INSERM. |
| − | The laboratory is equipped with stimulation apparatus that includes video projection and Stax calibrated system for auditory stimulation. It belongs to the Aix-Marseille University and is accessible to all teams involved in fundamental and clinical brain research. | + | The laboratory is equipped with stimulation apparatus that includes video projection and Stax calibrated system for auditory stimulation. It belongs to the Aix-Marseille University and is accessible to all teams involved in fundamental and clinical brain research, and has the label "plateforme technologique". The platform is involved in a day hospital with AP-HM for presurgical evaluation of patients with epilepsy |
| − | The research team of the MEG laboratory is specialized in confronting results of source localization to intracerebral EEG | + | The research team of the MEG laboratory is specialized in confronting results of source localization to intracerebral EEG and in designing and optimizing signal processing methods for multimodal functional investigation of human cerebral activity (pathological and physiological). See [[Dynamap]] page. |
| − | + | For a list of publications from the teams associated with the MEG platform, see [[Publications]]. | |
| − | + | For list of equipement and how to submit a project, see [https://www.ibisa.net/plateformes/magneto-encephalographie-meg-630.html IBISA website]. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | = | + | <br clear=all> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | =News and Events= | |
| + | The team was present in two symposia at [https://www.biomag2024.org/cms/ BIOMAG 2024] | ||
| − | + | The Amidex industrial chair 'NewMeg Marseille' will start soon.... | |
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <!--[[MEG:Formations_et_Animations| '''Prochaine réunion du Club MEG''']]--> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| − | + | ==Recent Publications== | |
| + | López-Madrona VJ, Medina Villalon S, Badier JM, Trébuchon A, Jayabal V, Bartolomei F, Carron R, Barborica A, Vulliémoz S, Alario FX, Bénar CG. [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35766240/ Magnetoencephalography can reveal deep brain network activities linked to memory processes.] Hum Brain Mapp. 2022 Oct 15;43(15):4733-4749. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25987. Epub 2022 Jun 29. PMID: 35766240 | ||
| − | [https:// | + | Velmurugan J, Badier JM, Pizzo F, Medina Villalon S, Papageorgakis C, López-Madrona V, Jegou A, Carron R, Bartolomei F, Bénar CG. [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36270623/ Virtual MEG sensors based on beamformer and independent component analysis can reconstruct epileptic activity as measured on simultaneous intracerebral recordings.] Neuroimage. 2022 Dec 1;264:119681. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119681. Epub 2022 Oct 18. PMID: 36270623 |
| − | [[ | + | Pizzo F et al [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30814498 Deep brain activities can be detected with magnetoencephalography]. Nat Commun. 2019 commented in |
| + | <small>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31203661 Addressing a Deep Problem With Magnetoencephalography]. Englot DJ. Epilepsy Curr. 2019 | ||
| − | + | see full list of [[Publications]]. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [ | + | ==PAST Events== |
| + | * PracticalMEEG [https://practicalmeeg2022.org/bouquet/ Anywave session] | ||
| − | [ | + | * BIOMAG 2022 Contest [[link=AnyWave:BIOMAG|Click to access the BIOMAG Contest page]]<br/> |
| − | + | ||
| − | [ | + | * Article on MEG in "la Marseillaise", in the context of ILCB opening: [[File:article ILCB la Marseillaise.pdf|Article sur centre MEG dans la Marseillaise]] |
| + | * '''[[EPJB2017|Ecole Pratique Jean Bancaud, Antibes 15-17 mai 2017]]''' | ||
| − | + | * Connectivity training with Fieldtrip 21-22 novembre 2016 [[File:Fiche annonce - Connectivité en MEG et EEG - 2016.pdf]] external link [[http://www.fieldtriptoolbox.org/workshop/marseille2016b]] | |
| − | [ | + | |
| − | [ | + | =The AnyWave Software= |
| + | [[Image:AnyWave.png|left|600px|link=AnyWave|Click to go to the AnyWave section]] | ||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| − | [ | + | =Staff= |
| + | [[JM_Badier|Jean-Michel Badier]], technical director | ||
| − | + | Bruno Colombet, software developer | |
| − | + | Samuel Medina-Villalon, Engineer AP-HM | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [http:// | + | [http://meg.univ-amu.fr/wiki/CG_Benar Christian Bénar], scientific director |
| − | [ | + | [[File:logos wiki 2024.jpg|1200px]] |
Latest revision as of 09:14, 20 September 2024
The Marseille MEG platform.
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) consists in recording brain magnetic activity. This activity is the counterparts of the electrical activity that originate from the brain, the well-known EEG. These techniques are the only ones that are directly related to the neural activity and have enough time resolution to track brain activity. One of the great advantages of the MEG other EEG is the very small effect of the conductivity of the different media of the head, especially the skull, compared to EEG.
The MEG laboratory of Marseille uses a 248 magnetometers MEG system (4D Neuroimaging magnes 3600). It is part of the Institut de Neurosciences des Systèmes (INS, Head V. Jirsa), and is installed within the Neurophysiology department of the Timone hospital (Head: F. Bartolomei). The system was co-financed by: Conseil Régional PACA, Conseil Général 13, Conseil Général 06, Marseille Provence Métropole, INSERM, CNRS, INRIA. It is currently co-financed by Aix-Marseille Université (though France Life Imaging) and INSERM.
The laboratory is equipped with stimulation apparatus that includes video projection and Stax calibrated system for auditory stimulation. It belongs to the Aix-Marseille University and is accessible to all teams involved in fundamental and clinical brain research, and has the label "plateforme technologique". The platform is involved in a day hospital with AP-HM for presurgical evaluation of patients with epilepsy
The research team of the MEG laboratory is specialized in confronting results of source localization to intracerebral EEG and in designing and optimizing signal processing methods for multimodal functional investigation of human cerebral activity (pathological and physiological). See Dynamap page.
For a list of publications from the teams associated with the MEG platform, see Publications.
For list of equipement and how to submit a project, see IBISA website.
News and Events
The team was present in two symposia at BIOMAG 2024
The Amidex industrial chair 'NewMeg Marseille' will start soon....
Recent Publications
López-Madrona VJ, Medina Villalon S, Badier JM, Trébuchon A, Jayabal V, Bartolomei F, Carron R, Barborica A, Vulliémoz S, Alario FX, Bénar CG. Magnetoencephalography can reveal deep brain network activities linked to memory processes. Hum Brain Mapp. 2022 Oct 15;43(15):4733-4749. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25987. Epub 2022 Jun 29. PMID: 35766240
Velmurugan J, Badier JM, Pizzo F, Medina Villalon S, Papageorgakis C, López-Madrona V, Jegou A, Carron R, Bartolomei F, Bénar CG. Virtual MEG sensors based on beamformer and independent component analysis can reconstruct epileptic activity as measured on simultaneous intracerebral recordings. Neuroimage. 2022 Dec 1;264:119681. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119681. Epub 2022 Oct 18. PMID: 36270623
Pizzo F et al Deep brain activities can be detected with magnetoencephalography. Nat Commun. 2019 commented in Addressing a Deep Problem With Magnetoencephalography. Englot DJ. Epilepsy Curr. 2019
see full list of Publications.
PAST Events
- PracticalMEEG Anywave session
- BIOMAG 2022 Contest Click to access the BIOMAG Contest page
- Article on MEG in "la Marseillaise", in the context of ILCB opening: File:Article ILCB la Marseillaise.pdf
- Connectivity training with Fieldtrip 21-22 novembre 2016 File:Fiche annonce - Connectivité en MEG et EEG - 2016.pdf external link [[1]]
The AnyWave Software
Staff
Jean-Michel Badier, technical director
Bruno Colombet, software developer
Samuel Medina-Villalon, Engineer AP-HM
Christian Bénar, scientific director