Difference between revisions of "AnyWave:WriteMatlabScripted"
(M) |
(→main.m) |
||
| (75 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
This section targets people who have a good knowledge and practice of the MATLAB programming language.<br/> | This section targets people who have a good knowledge and practice of the MATLAB programming language.<br/> | ||
| − | The purpose is to explain how to write a MATLAB function that will be the heart of | + | The purpose is to explain how to write a MATLAB function that will be the heart of a plug-in executed in MATLAB by AnyWave.<br/> |
We will also explain how to create a text file to describe our plug-in to AnyWave<br/> | We will also explain how to create a text file to describe our plug-in to AnyWave<br/> | ||
| + | The AnyWave-MATLAB API consists in a set of MATLAB functions. They will be described in details in a dedicated section.<br/> | ||
| − | The | + | =Setup the plugin folder= |
| + | The first thing to do is to create the basic structure for a plug-in.<br/> | ||
| + | A MATLAB Scripted plug-in is very simple: it is a folder containing at least two files.<br/> | ||
| − | + | Let's begin by creating a folder (called MyPlugin) somewhere on the computer.<br/> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | Let's begin by creating a folder somewhere on the computer | + | |
This can be done in MATLAB: create a folder and create a new function called '''main''' in that folder.<br/> | This can be done in MATLAB: create a folder and create a new function called '''main''' in that folder.<br/> | ||
The main function is '''MANDATORY'''. It will be the main function AnyWave will call to execute our plugin.<br/> | The main function is '''MANDATORY'''. It will be the main function AnyWave will call to execute our plugin.<br/> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 28: | ||
name = My Matlab Plugin | name = My Matlab Plugin | ||
description = I am a plug-in written in Matlab | description = I am a plug-in written in Matlab | ||
| + | category = Process:MATLAB:My MATLAB Plugin | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | The syntax is to set keywords and values.<br /><br /> | ||
| − | + | Here we have three keywords (name, description, category).<br /> | |
| − | + | Two keywords are mandatory : name and description. Other keywords are optional.<br /> | |
| − | = | + | ==desc.txt keywords== |
| − | + | Some keywords may have several values. Separate the values by the colon character ''':''' <br/> | |
| − | + | The table below shows all the keywords handled by AnyWave and their functions.<br/> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | The table below shows | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! keyword !! description !! type |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | name || the name of your plugin. Must be unique.|| MANDATORY |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | description || short description || MANDATORY |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | category || Where to link the plugin in AnyWave menus || OPTIONAL |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | input_flags || what is required for input || OPTIONAL |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | flags || The plugin special flags || OPTIONAL |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ===category=== |
| − | AnyWave | + | '''category:''' It tells AnyWave where the plug-in will appear in the menus. Here, we decided to make it appear under the Python sub-menu in the Processes main menu.<br /> |
| − | + | The category feature is usefull to separate plug-ins by theme.<br/> | |
| − | The | + | Three category keywords are recognized:<br/> |
| − | <br/> | + | * Process : The plug-in will be set in the Processes menu with a subcategory and a name, for example 'Process:Correlation:Compute correlation' |
| − | '' | + | * File: The plug-in will be set in the File Menu under the Export sub-menu. Example : 'File:Export to file.' |
| − | + | * View: The plug-in will be set in the View Menu. Example : 'View:Launch 3D viewer' | |
| − | + | If no category is specified, AnyWave will set the plug-in in the Processes menu using the name defined in the file.<br/> | |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===input_flags=== | |
| − | + | '''input_flags:''' a list a ":" separated strings that set the input flags for the plugin.<br/> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! input_flag !! description |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | GetAllMarkers || AnyWave will copy all the markers and set them as input for the plugin. This will impact aw_getmarkers() function. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | GetDurationMarkers || AnyWave will copy markers with a duration and set them as input. This will impact aw_getmarkers() function |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | ProcessIgnoresChannelSelection || The plugin will be run without using the selected channels as input by default. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | ProcessRequiresChannelSelection || The plugin will only run if the user has selected channels. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | GetAsRecordedChannels || AnyWave will copy all the as recorded channels found in the current file as input for the plugin. This will impact aw_getdata() function. |
| − | |- | + | |- |
| − | | | + | | GetCurrentMontage || AnyWave will copy the current montaged channels and set them as input for the plugin. This will impact aw_getdata() function. |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | Example of desct.txt with input_flags:<br/> | |
| − | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="text"> | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang=" | + | name = MyPlugin |
| − | + | description = do something in MATLAB | |
| − | + | category = Process:Test:MyPlugin | |
| − | + | input_flags = ProcessIgnoresChannelSelection:GetAllMarkers | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | ===flags=== | |
| − | + | flags are used to configure the plugin capabilities.<br/> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | === | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! flag !! description |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | NoDataRequired or ProcessDoesntRequireData || indicates the plugin doesn't need a file to be open in AnyWave to run. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | CanRunFromCommandLine || indicates that the plugin can also run in batch mode and using the command line. |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | =main.m= | |
| − | + | This is the entry point function called by AnyWave.<br/> | |
| − | + | Depending on the type of plugin you are writing, you may have to setup some variables in this file as an initialisation:<br> | |
| + | Indeed, you may decide to compile your plugin to distribute it as a standalone software. In this case, use the following code in your main.m:<br/> | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="matlab"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="matlab"> | ||
| − | function main() | + | function main(varargin) |
| − | + | global args; | |
| − | + | if isdeployed | |
| − | + | % STANDALONE AnyWave Plugin code | |
| − | + | global host; | |
| − | + | global port; | |
| − | + | global pid; | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | if (nargin < 3) | |
| − | + | error('missing arguments.'); | |
| − | + | end | |
| + | host = varargin{1}; | ||
| + | port = str2num(varargin{2}); | ||
| + | pid = str2num(varargin{3}); | ||
| + | if (nargin > 3) | ||
| + | args = varargin{4}; | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | |||
| + | assignin('base', 'host', host); | ||
| + | assignin('base', 'port', port); | ||
| + | assignin('base', 'pid', pid); | ||
| + | assignin('base', 'args', args); | ||
| + | % end of STANDALONE AnyWave Plugin code | ||
end | end | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | =Copy the plug-in to the right location= | |
| + | We are ready to add the plug-in to AnyWave. | ||
| − | + | Copy the folder MyPlugin to your user's AnyWave plugins directory. Remember to place it in the Matlab subfolder. | |
| − | + | For example on Windows: | |
| + | [[File:Matlab3.png|center]] | ||
| − | + | As you can see MyPlugin is located in the user's AnyWave path for Matlab Scripted plug-ins. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | =Use the plug-in in AnyWave= | |
| − | + | Launch AnyWave: the plug-in should be shown as available. | |
| − | + | [[File:Matlab4.png|center]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Latest revision as of 14:17, 30 March 2020
Contents
Introduction
This section targets people who have a good knowledge and practice of the MATLAB programming language.
The purpose is to explain how to write a MATLAB function that will be the heart of a plug-in executed in MATLAB by AnyWave.
We will also explain how to create a text file to describe our plug-in to AnyWave
The AnyWave-MATLAB API consists in a set of MATLAB functions. They will be described in details in a dedicated section.
Setup the plugin folder
The first thing to do is to create the basic structure for a plug-in.
A MATLAB Scripted plug-in is very simple: it is a folder containing at least two files.
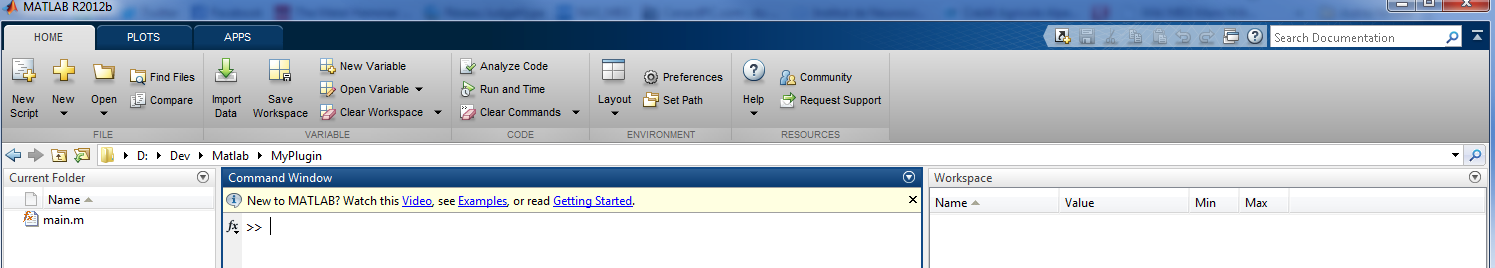
Let's begin by creating a folder (called MyPlugin) somewhere on the computer.
This can be done in MATLAB: create a folder and create a new function called main in that folder.
The main function is MANDATORY. It will be the main function AnyWave will call to execute our plugin.
As shown in the image above, a MyPlugin folder has been created and a main function was added.
We are now ready to write our first Matlab plug-in!!
Refer to the AnyWave-MATLAB functions section to learn how to program a plug-in that will communicate with AnyWave.
Writing the desc.txt file
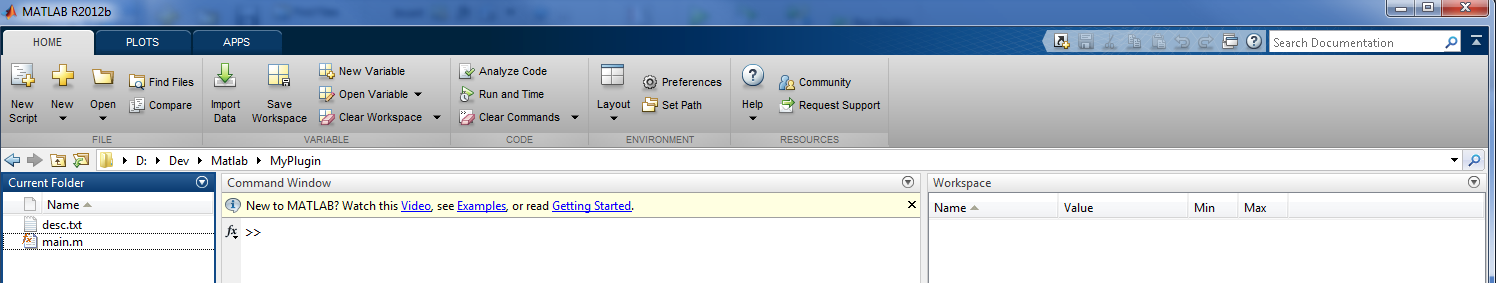
We have written the MATLAB code and now all we have to do is to create a descriptive text file to inform AnyWave about our plug-in.
Let's dot it in Maltab:
The file must be named desc.txt and may looks like:
name = My Matlab Plugin description = I am a plug-in written in Matlab category = Process:MATLAB:My MATLAB Plugin
The syntax is to set keywords and values.
Here we have three keywords (name, description, category).
Two keywords are mandatory : name and description. Other keywords are optional.
desc.txt keywords
Some keywords may have several values. Separate the values by the colon character :
The table below shows all the keywords handled by AnyWave and their functions.
| keyword | description | type |
|---|---|---|
| name | the name of your plugin. Must be unique. | MANDATORY |
| description | short description | MANDATORY |
| category | Where to link the plugin in AnyWave menus | OPTIONAL |
| input_flags | what is required for input | OPTIONAL |
| flags | The plugin special flags | OPTIONAL |
category
category: It tells AnyWave where the plug-in will appear in the menus. Here, we decided to make it appear under the Python sub-menu in the Processes main menu.
The category feature is usefull to separate plug-ins by theme.
Three category keywords are recognized:
- Process : The plug-in will be set in the Processes menu with a subcategory and a name, for example 'Process:Correlation:Compute correlation'
- File: The plug-in will be set in the File Menu under the Export sub-menu. Example : 'File:Export to file.'
- View: The plug-in will be set in the View Menu. Example : 'View:Launch 3D viewer'
If no category is specified, AnyWave will set the plug-in in the Processes menu using the name defined in the file.
input_flags
input_flags: a list a ":" separated strings that set the input flags for the plugin.
| input_flag | description |
|---|---|
| GetAllMarkers | AnyWave will copy all the markers and set them as input for the plugin. This will impact aw_getmarkers() function. |
| GetDurationMarkers | AnyWave will copy markers with a duration and set them as input. This will impact aw_getmarkers() function |
| ProcessIgnoresChannelSelection | The plugin will be run without using the selected channels as input by default. |
| ProcessRequiresChannelSelection | The plugin will only run if the user has selected channels. |
| GetAsRecordedChannels | AnyWave will copy all the as recorded channels found in the current file as input for the plugin. This will impact aw_getdata() function. |
| GetCurrentMontage | AnyWave will copy the current montaged channels and set them as input for the plugin. This will impact aw_getdata() function. |
Example of desct.txt with input_flags:
name = MyPlugin description = do something in MATLAB category = Process:Test:MyPlugin input_flags = ProcessIgnoresChannelSelection:GetAllMarkers
flags
flags are used to configure the plugin capabilities.
| flag | description |
|---|---|
| NoDataRequired or ProcessDoesntRequireData | indicates the plugin doesn't need a file to be open in AnyWave to run. |
| CanRunFromCommandLine | indicates that the plugin can also run in batch mode and using the command line. |
main.m
This is the entry point function called by AnyWave.
Depending on the type of plugin you are writing, you may have to setup some variables in this file as an initialisation:
Indeed, you may decide to compile your plugin to distribute it as a standalone software. In this case, use the following code in your main.m:
function main(varargin) global args; if isdeployed % STANDALONE AnyWave Plugin code global host; global port; global pid; if (nargin < 3) error('missing arguments.'); end host = varargin{1}; port = str2num(varargin{2}); pid = str2num(varargin{3}); if (nargin > 3) args = varargin{4}; end assignin('base', 'host', host); assignin('base', 'port', port); assignin('base', 'pid', pid); assignin('base', 'args', args); % end of STANDALONE AnyWave Plugin code end
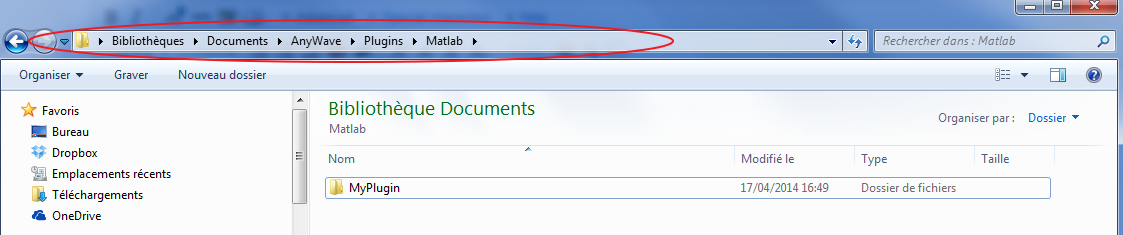
Copy the plug-in to the right location
We are ready to add the plug-in to AnyWave.
Copy the folder MyPlugin to your user's AnyWave plugins directory. Remember to place it in the Matlab subfolder. For example on Windows:
As you can see MyPlugin is located in the user's AnyWave path for Matlab Scripted plug-ins.
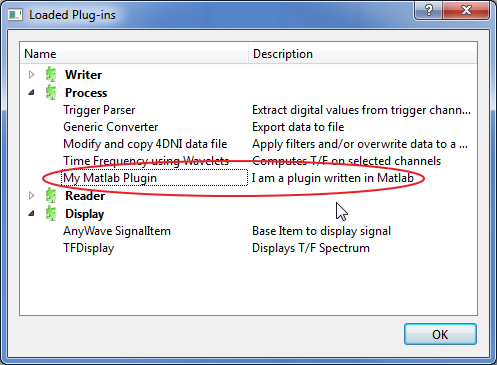
Use the plug-in in AnyWave
Launch AnyWave: the plug-in should be shown as available.